Reducing product loss & human error in pharmaceutical fermentation
Table of contents
ShowThe fact that the pharmaceutical manufacturing process, including pharmaceutical fermentation, is still prone to human error and product loss can be more than frustrating. This is even more true when dealing with issues that are near and dear to you, when your aim is to increase efficiency while reducing overhead costs.
You may also want to improve sustainability while reducing your company’s environmental impact. In microbial fermentation, both human error and potential product loss stand in the way of efficiency, while compromising quality.
But it doesn’t have to stay that way, and it doesn’t take that much to implement changes. The challenges can be overcome by moving to automated processes that eliminate the need for slow and error-prone manual handling. Adopting automated end-to-end solutions based on single-use technologies minimizes, if not eliminates, human error and product loss.
Single-use solutions are easily adaptable and scalable, resulting in an overall smaller ecological footprint and greater efficiency at an overall lower price.
Challenges in the fermentation of pharmaceutical compounds
Microbial fermentation for pharmaceutical APIs, bioconjugates or smaller biologics can be a challenging process. Apart from the obvious - tight development timelines and budgets that are often limited - there are other issues that need to be addressed:
- The risk of contamination from other microorganisms, which can affect the quality and purity of the final product. The best scenario would be to minimize all manual handling and to introduce protection that is not only efficient but also scalable.
- The potential need to scale up: Different production volumes may entail different equipment, as well as process parameters, thus calling for agile production systems.
In order to tackle the various challenges, more and more manufacturers are looking at implementing fully automated processes or outsourcing to external CDMOs.
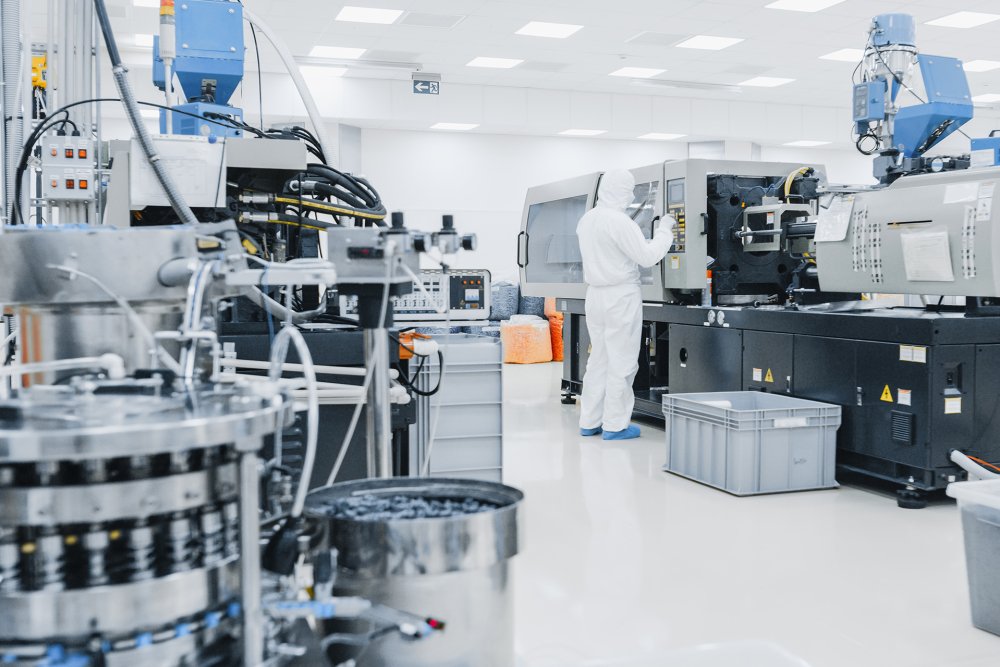

Role of CDMOs in fermentation
With their dedicated facilities and automated processes, well-established CDMOs are able to flexibly alter their fully sterile production lines to meet the increasing demand of smaller, more diverse projects. In addition, they can rapidly expand their capabilities and are thus able to deliver technically advanced services at scale.
Obviously, those third-party service providers need to demonstrate a certain skill set in order to be of real value. Among the necessary skills, or rather characteristics, three Es - experience, expertise and efficiency - as well as flexibility are key. With their fully automated end-to-end solutions, cGMP compliant CDMOs will be able to scale up from lab-scale fermentation to commercial production. In doing so, they must also maintain sterility, and achieve consistent product quality in microbial cGMP production.
Minimize human errors
Consider that to date, approximately 36% of all filling errors in pharmaceutical manufacturing sites are caused by human error. Those errors can have severe consequences for the patient relying on a certain medical product. In addition to facing legal liabilities, including product liability lawsuits or breach of contract claims, the manufacturer will most likely suffer significant financial losses.
The replacement of manual handling steps by fully automated and digitized processes is a promising approach. Better known as Pharma 4.0, it will help to reduce human error. In addition, it will provide valuable support for root cause analysis procedures as well as sustainable CAPAs (Corrective Actions, Preventive Actions). Done right, it will enable faster decision-making, and provide in-line and on-time control over business, operations, quality, and regulatory compliance. 1
Eliminating product loss
Apart from reducing human error and eliminating product loss during your fermentation process, reliable and yet vendor-independent single-use end-to-end solutions can also push your output to the next level. One of the main reasons for product loss is contamination during the actual fermentation process but also during storage and shipping.
This is why smart logistics solutions are needed in addition to automated processes. They include advanced systems that can handle a range of volumes and enable easy and straightforward scaling in bioprocessing.
If you are planning to move to modular and agile single-use technologies, you will want to aim for a smooth and seamless transition. In order for this to happen, compatibility with existing systems should be as important as compliance with all required regulations and cGMP practices. Secondly, these single-use solutions should provide for protective packaging to prevent product loss. Ideally, it should be adaptable to different sizes and container types.
Single Use Support’s RoSS® Shell is the answer. Proven as the safest transport solution for all single-use bags, the innovative shell protects bioprocess containers of all sizes from shock and vibration during freezing, transport and storage. With over 200,000 shells sold, measured product loss is less than 0.001%.
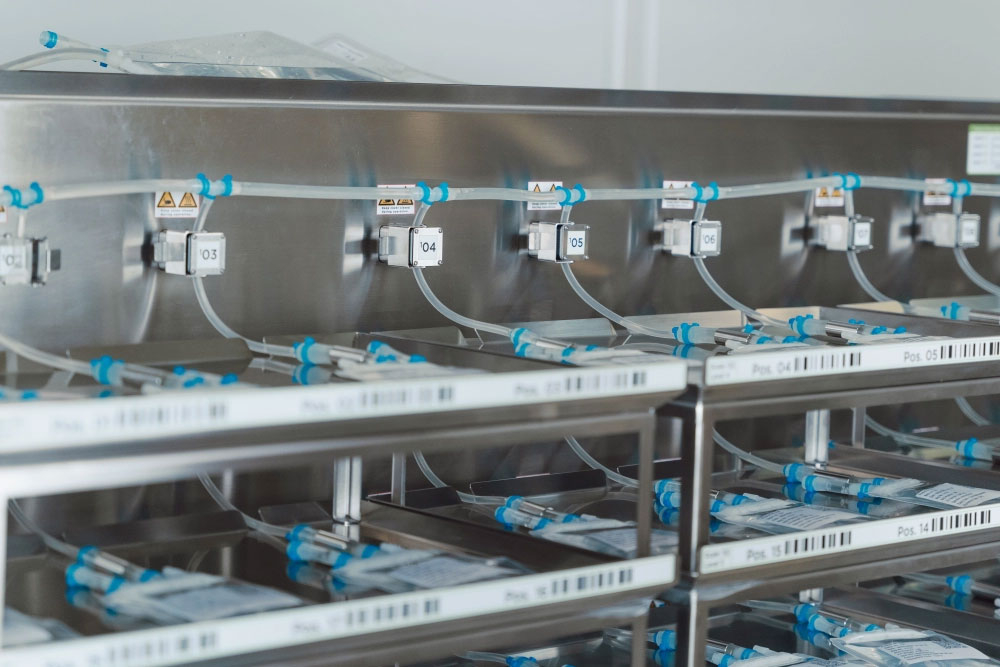
Efficient fermentation of large volumes with single-use technology
After a hiatus of several years, microbial fermentation is on the rise again, and this is not surprising: The process is highly efficient and cost-effective, as microbes can be grown in large quantities. It is an inexpensive and efficient alternative to cell-based or other production methods. Its renewed popularity calls for equally inexpensive and efficient cold chain handling and logistics solutions, which can be provided by single-use technologies.
Single-use bags, for instance, can be filled and frozen with volumes of 1,000 L or more within eight hours in a monitored, fully automated, process. They can then be sent on their way for completion, final conjugation and further clinical manufacturing.

- What is the leading cause of filling errors, https://www.aspenalert.com/asq-790-2022-0318-what-is-the-leading-cause-of-filling-errors-at-your-site-please-comment-on-your-experiences, Published 28.02.2023










