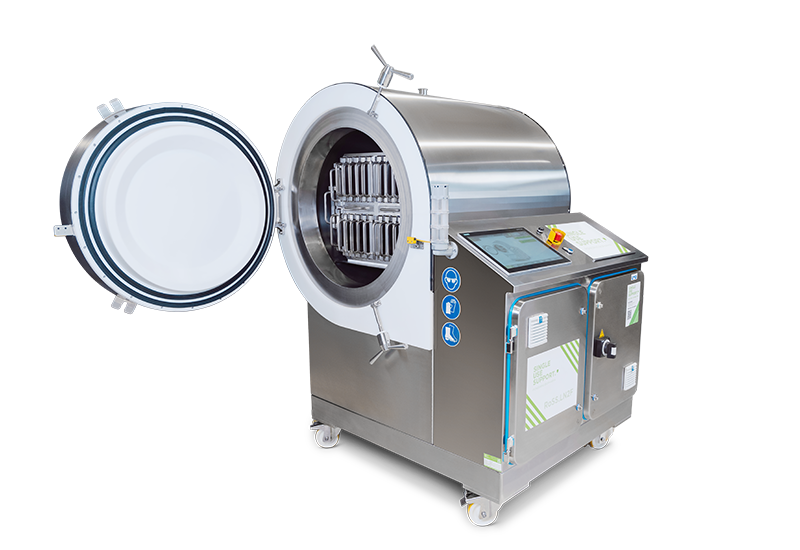
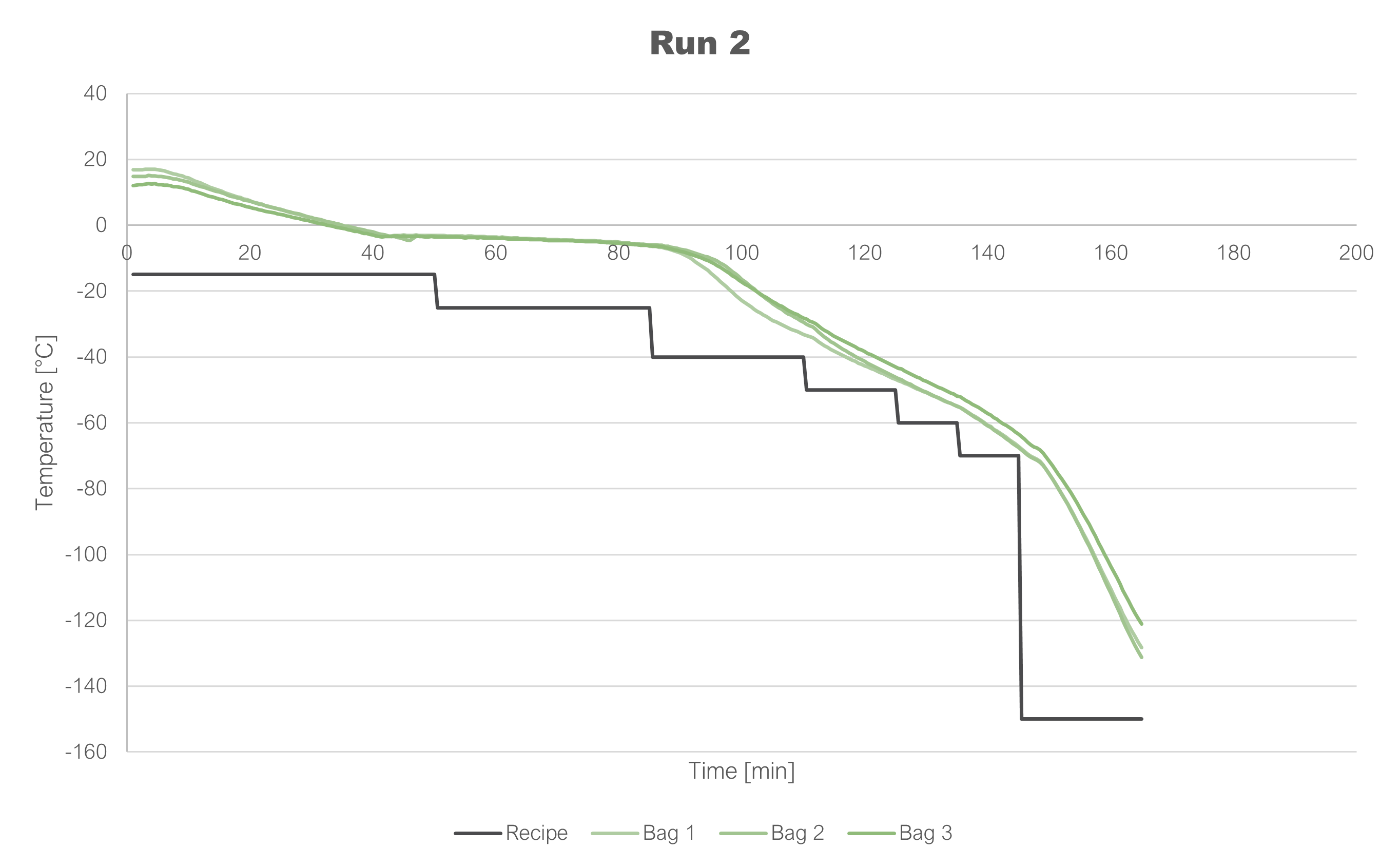
Controlled rate freezing of cells
Downloads

Datasheet: RoSS.LN2F
Please fill out the form below to download this file.

Datasheet: RoSS.LN2F

Study: Increased CHO Cell Viability with Controlled Liquid Nitrogen Freezer
Please fill out the form below to download this file.

Study: Increased CHO Cell Viability with Controlled Liquid Nitrogen Freezer

App Note: "Bestcellers": Controlled Filling & Freezing of Cells
Please fill out the form below to download this file.

App Note: "Bestcellers": Controlled Filling & Freezing of Cells