Dual Sourcing: Strengthening the Pharmaceutical Supply Chain for Single-Use Assemblies
Table of contents
ShowSingle Sourcing vs. Dual Sourcing
Do you remember when lead times were months instead of weeks? During the COVID-19 pandemic, biomanufacturers faced several significant supply chain challenges:
- Lockdowns and restrictions led to disruptions in transportation and logistics, complicating the movement of raw materials and finished products.
- Increased demand for certain biomanufactured products such as vaccines or therapeutics often resulted in shortages of critical raw materials with long lead times.
For instance, bioprocess containers experienced lead times ranging from one to four months. Essential items like filter capsules, isolator technology, and assemblies sometimes had lead times extending from 14 up to 60 weeks. Additionally, there was a significant shortage of supplier specialists and engineers, which further complicated the process of setting up and stabilizing biomanufacturing processes. Increased shipping times and costs due to port congestion and limited freight capacity exacerbated these supply chain issues.
These challenges prompted many biomanufacturers to rethink their supply chain strategies, resulting in an emphasis on local sourcing, flexibility, and resilience to better prepare for future disruptions. This scenario brings us to dual sourcing and its capability to strengthen the robustness of the pharmaceutical supply chain.
Benefits of Dual Sourcing and Multi Sourcing
What do dual and multi-sourcing entail? These strategies are one of the core methods to strengthen the pharmaceutical supply chain.
- Dual sourcing strategies involve obtaining a particular product or single-use system from two suppliers, ensuring continuity of supply for critical components.
- Multi sourcing, on the other hand, involves sourcing from multiple suppliers, providing diverse quality levels, prices, or innovative features. Both strategies are vital for enhancing resilience and adaptability in global markets characterized by rapid changes and uncertainties.
Vendor independence is a crucial factor for enhancing supply chain robustness. It allows companies to negotiate better prices and terms, switch suppliers if costs rise, and maintain competitive expenses. In a dynamic environment where demand can fluctuate rapidly, having multiple vendors enables biomanufacturers to flexibly scale operations, avoiding bottlenecks and delays. Maintaining relationships with various vendors also provides more data and insights about the supply chain, improving decision-making, forecasting, and planning. Collaboration with different vendors can lead to better products and more efficient manufacturing processes.

Challenges in Pharmaceutical Procurement Strategies
However, dual and multi-sourcing programs present several challenges. A procurement strategy is much more than simply selecting new suppliers, as it involves ensuring timely delivery of quality medicines, and managing relationships to control costs.
The cost of validating a second source can be high, requiring evaluation of each supplier's materials, processes, and facilities. Transferring processes between suppliers can be complex due to unique technologies and equipment. Managing relationships with multiple suppliers increases communication complexity and administrative overhead. Despite these challenges, fostering competition between suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms.
Most dual and multi-sourcing programs are carried out through requests for quotations (RFQs) for single-use assemblies. Potential suppliers are identified based on their capabilities, compliance with regulatory requirements, and previous performance. The goal is to select suppliers that can meet quality standards, desired delivery times, and overall price expectations. The biopharmaceutical industry is highly regulated, necessitating strict adherence to quality and regulatory standards to ensure compliance.

Supply Chain Resilience with Agnostic Integrator
An agnostic integrator plays a crucial role in this context. As a supplier-independent manufacturer, they provide customized single-use systems tailored to specific client needs, accommodating various biopharmaceutical processes. Their independence allows them to select the best components and materials from multiple sources, ensuring compatibility and functionality. They ensure their products meet stringent industry regulations and quality standards, handling testing and validation to provide assurance of correct and safe functioning in bioprocessing applications. Flexibility in testing and validation is a core competence of an integrator to meet quality requirements.
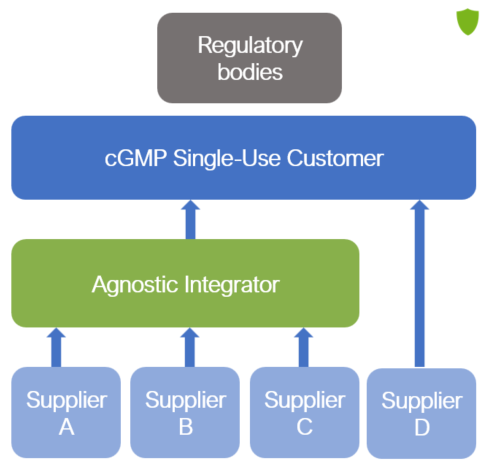
Single Use Support as Robust Integrator
In conclusion, understanding the requirements for dual and multi-sourcing is essential for producing sterile consumables and single-use assemblies according to industry standards for filling systems, as well as upstream, downstream, and fill-finish processes.
One of Single Use Support’s core competencies is creating robust solutions using different market components swiftly. Our experience with multi-sourcing programs has provided insights into keeping these programs efficient and cost-effective. Partnering closely with customers and suppliers requires considerable effort but leads to more resilient and adaptable supply chains.









