CAR-T manufacturing: process and supply chain strategies
Table of contents
ShowMastering the complex CAR T manufacturing process and the associated supply chain challenges in the cell and gene area are the major bottlenecks during the large-scale commercialization of highly promising CAR T cell products.
This autologous transgene cellular therapy approach has gained US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval for relapsed or refractory blood malignancies such as B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL), in the instance of Novartis’ Kymriah, which was developed in collaboration with the University of Pennsylvania. Numerous clinical trials are currently ongoing to ascertain whether additional indications could benefit from CAR T cell cancer immunotherapy.1 2 3
CAR T manufacturing process
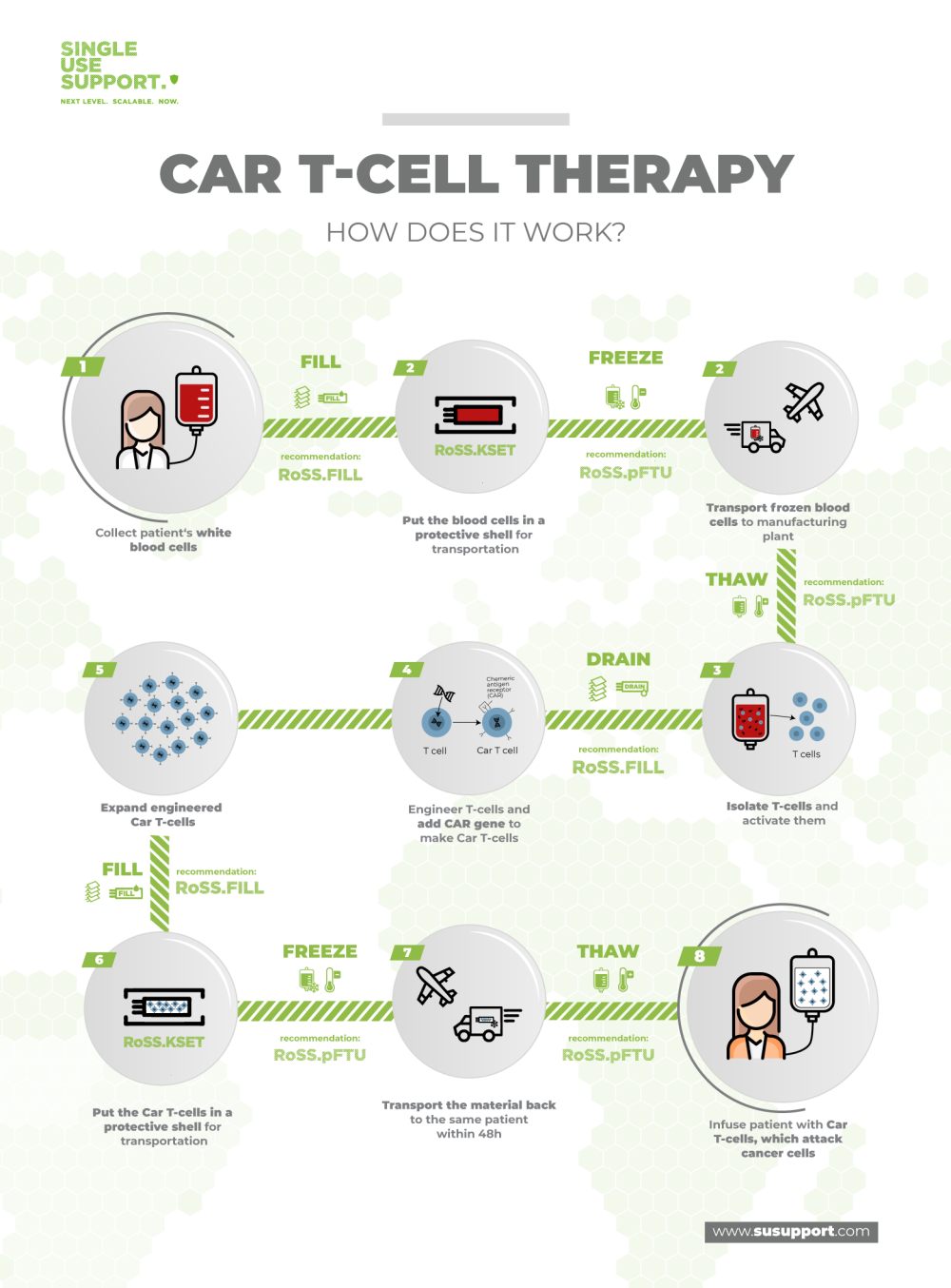
The CAR T manufacturing process is a very sensitive and highly complex endeavor. In brief, the patient’s T lymphocytes are removed from the bloodstream and reprogrammed in the laboratory to become very alert and aggressive towards cancer cells through expression of chimeric antigen receptors, resulting in very effective antitumor drugs.
Due to the intricacies of the human immune system, each patient needs an individualized batch of chimeric antigen receptor T cells, implying that these are no off-the-shelf drugs. Each batch of CAR T cells is a distinct manufacturing campaign with its own supply chain that begins at the patient.
Personalized supply chain for CAR T cell therapy
The power of CAR-T therapy lies in the fact that every therapy is tailored to meet each individual patient's needs. The flip side of the coin is the complex supply chain situation this implies: Every patient contributes source material that has to be shipped under cryogenic and aseptic conditions to the manufacturing facility in order to manufacture one distinct batch of extremely valuable, unique drug substance.
Any faults along the supply chain may lead to severe consequences for the patient. Therefore, biopharmaceutical companies undertake great efforts to eliminate failure modes wherever possible and minimize all conceivable risks of the process.

Collection of CAR T cells from the patient
The first step in most CAR T cell manufacturing processes is the collection of T cells from the respective patients. This is done in a procedure named leukapheresis. Generally, apheresis is the removal of blood cells from peripheral blood, leukapheresis is the collection of leukocytes. Instruments such as CliniMACS Plus and Prodigy allow the isolation of specific subtypes of T cells.
Chemotherapy cycles that are performed prior to leukapheresis have been shown to reduce the viability of T cells and experts in oncology advise the early collection of T cells, prior to stem-cell transplants.
With the leukapheresis process, the individualized supply chain starts.4 5
Transportation of the collected T-cells to the lab
Next, the collected T cells are prepared for the transport from the healthcare site to the manufacturing facilities. In order to keep the cells viable, they are transferred into single use bags, which in turn are placed into protective shells and subsequently frozen, shipped and stored at ultra-cold temperatures (cryopreservation).

Download our App Note
APP NOTE: Controlled Filling & Freezing of Cells
Download our app note about Advanced Fluid Management for Cell Culture Freezing, Cell Banking and Cell Therapy.
CAR-T cell therapy development
At the cell therapy manufacturing site, the CAR-T cells are thawed for modification. The next step is viral transduction and involves the actual gene transfer into T cells using viral vectors such as lentiviral vectors. This exposure to reprogramming lentivirus leads to genetic modification of the TCRs of the cells, resulting in anti-CD19 CAR T cell activation towards tumor cells.
Next, ex vivo proliferation of CAR T cells is performed in cell culture in bioreactors (CAR T cell expansion) to obtain sufficient amounts of the biopharmaceutical material. Since this workflow is adherent to good manufacturing practice (GMP), numerous testings, characterizations and quality control measures are performed on the CAR T cells to ensure full satisfaction of all regulatory requirements. These requirements include the absence of mycoplasma, minimal variability of phenotypes and cell types, low endotoxin mediated toxicity and many more.6
Transportation of CAR T cells from the lab to the patient
When the individualized CAR T cell immunotherapy product has passed all tests, the cells are again packaged in medical devices, put into their protective sleeves and brought to cryogenic temperatures for transportation to the medical center. Orchestration of all participants is very important to ensure timely delivery and appropriate storage conditions before the product is administered to the patient.
Considerations for a safe supply chain
In order to set up safe supply chains, a complex network of interdependent variables must be orchestrated:
- schedules of patients, healthcare providers, manufacturing facilities
- demand volatility
- cost optimization
- patient safety and security
The ultimate goal is an efficient end-to-end collaboration of all participants. Innovative products that support real-time tracking of processes and data analysis using cloud computing offers powerful digital solutions to the supply chain problem.
Single Use Support’s part in CAR T manufacturing process and supply chain
Single Use Support offers a comprehensive product portfolio that facilitates the development and upscaling of CAR T manufacturing processes. Moreover, its products are highly compatible in order to enable a smooth workflow along the complex vein-to-vein supply chain. For instance, RFID tags on every component take care of automation regarding the real-time documentation of passing checkpoints during handling, transfer volumes, temperatures, and gapless recording of the chain of identity of each batch.
Single-use components lead to more efficient use of space at manufacturing sites, facilitate scalable operations, e.g. with the Single Use Support freeze-thaw-platforms, and offer end-to-end process solutions for cell and gene therapies.
- Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells for Sustained Remissions in Leukemia, http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1407222, Published 2014-10-15
- Mesothelin-Specific Chimeric Antigen Receptor mRNA-Engineered T Cells Induce Antitumor Activity in Solid Malignancies, http://dx.doi.org/10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-13-0170, Published 2013-12-20
- Mechanisms of resistance to CAR T cell therapy, http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41571-019-0184-6, Published 2019-03-05
- , Published 1970-01-01
- Apheresis Techniques and Cellular Immunomodulation, http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-9987.1997.tb00137.x, Published 2007-11-14
- Genetically modified T cells in cancer therapy: opportunities and challenges, http://dx.doi.org/10.1242/dmm.018036, Published 2015-04-01