Regulations for Cryoprotectants in ATMP Cryopreservation
Table of contents
ShowCell viability is one of the cell product quality and regulatory parameter that determines therapeutic efficacy. For example, the FDA mandates a viability threshold of ≥ 80% for the release of CAR T cells.
Nevertheless, in clinical trials and in commercial contexts outside the United States, the specified cell viability requirement is set at ≥ 70%. Real-world data reveals comparable efficacy and safety profiles between CAR T cell infusions with 60% to 79% viable CAR T cells and those with over 80% viability1.
GMP Annex 1 on ATMP Cryopreservation
The difference requirements within ATMPs might result due to the different guidelines available and the confusion, when to apply what standards. In the past, guidelines designed for standard drugs were extended for the younger ATMPs, like Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guideline specific towards ATMPs were approved by the European Commission (EC) in 2017.
While EU GMP Annex 1 is considered nonbinding for ATMPs in Europe and the United States, questions arise regarding the relationship between Annex 1 and existing ATMP guidelines. The two most important standards for ATMPS are described in PIC/S Annex 2A: Manufacture of Advanced Therapy Medicinal Products for Human Use; and in Part IV- GMP Requirements for Advanced Therapy Medicinal Products of the EudraLex - Volume 4. EMA removed ATMPs from Annex 2 and made a new standalone set of regulations specific just for ATMPs in EudraLex Volume 4, Part IV.
In contrary, PIC/S (Pharmaceutical Inspection Co-operation Scheme) kept ATMP guidance in Annex 2 but split it into Annex 2A for ATMPs and Annex 2B for biological medicinal substances and products for human use. PIC/S Annex 2A PICS GMP Guide (Annexes) (pda.org) is different from the stand-alone EMA EudraLex rules, because it explicit refers and recommends the application in conjugation with PIC/S GMP guidelines and other Annexes, like Annex 1 for Sterile Medicinal Products. For example, in Annex 2A, chapter 3 states that `requirements of Annex 1 regarding the provision of closed system should be considered`. The reference to Annex 1 is not the case unless explicitly mentioned in EudraLex Part IV.2
Let’s have a look inside EudraLex Part IV for some relevant chapters from the point of cryopreservation.
Documentation: reports & traceability data
The level of documentation will vary depending on the product and stage of development. The records should enable the entire history of a batch to be traced. Additionally, the records/reports should form the basis for assessment of the suitability for certification and release of a particular batch.
As a minimum, the following should be documented: Receipt records for each delivery of raw materials, starting material, bulk, intermediate as well as primary packaging materials, batch processing record, results of release testing and on-going stability program.
A system that enables the bidirectional tracking of cells/tissues contained in ATMPs from the point of donation, through manufacturing, to the delivery of the finished product to the recipient should be created. Such system, which can be manual or electronic, should be established since the beginning of the manufacture of batches for clinical use. In accordance with Article 15 of Regulation 1394/2007, traceability information should also cover raw materials and all substances that come into contact with the cells or tissues. This Section describes the type and amount of data that must be generated and kept by manufacturers of ATMPs.2,3

- Seed lot and cell bank system: Request general evidence of the stability and recovery of seeds and banks. Preliminary stability data (e.g. from earlier phases of development or from suitable cell models) should be available before the product is used in a clinical trial, and the stability data should be built-up with real-life data as the clinical trial progresses.
- Equipment: The integrity of the equipment´s components should be verified as appropriate having regard to the specific risk of the product and the intended manufacturing process (e.g. ensuring structural integrity during freeze and thawing).
- Production: Measures to prevent cross-contamination appropriate to the risks identified should be put in place. Measures that can be considered to prevent cross-contamination include use of “closed systems” for processing and material/product transfer between equipment and recommends the utilisation of single use disposable technologies. ATMPs should be suitably packaged to maintain the quality of the product during storage, handling, and shipping. Particular attention should be paid to the closure of containers to ensure the integrity and quality of the product. For authorised ATMPs, the closure procedures should be validated, and the effectiveness should be 55 verified at appropriate intervals. Validation with surrogate materials is acceptable when materials are scarce.
- Validation of transport conditions: Transport conditions should be defined in writing. Adequacy of the defined transport conditions (e.g. temperature, type of container, etc.) should be demonstrated. Compliance with the defined transport conditions falls outside the responsibility of the manufacturer (unless such responsibility is assumed by means of contract).
- Automated production of ATMPs: Aseptic processing: The automated equipment should only be used under conditions that ensure aseptic processing (e.g. validation of cleaning processes, sterilisation of multiple-use materials that are in contact with the product, adequate checks of the integrity of the equipment, for example, by means of pressure-hold test or leak testing, etc.).
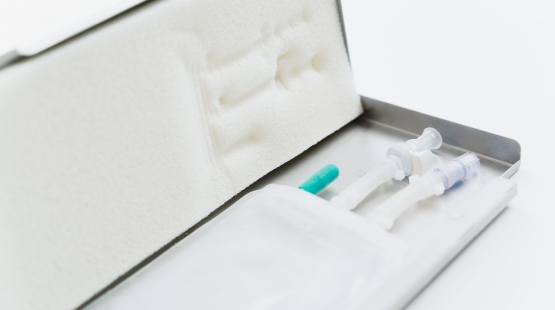
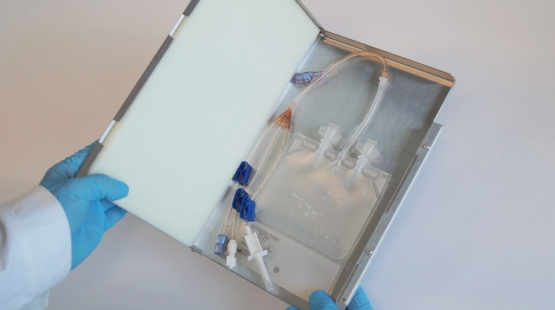
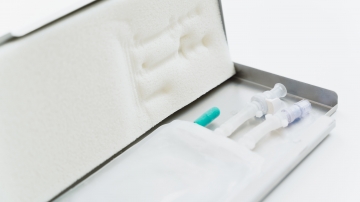
The role of aseptically closed single-use systems in cryopreservation process
Implementing fully automated and fully closed, single-use systems in the manufacturing process can help companies to follow the given regulations and thus improve their cGMP compliance. Manual processes are replaced by automated technologies and thus fulfil important factors for GMP such as reproducibility, standardization, and reduced risk. Validation of processes is very critical for regulatory compliance and to ensure that the ideal established cooling processes is followed during the real scenario cryopreservation to guarantee safety, effectiveness, and consistency.
The use of single use bags in combination with a metallic casing contributes to the safety, effectivity, and consistency of the validation for the cryopreservation process. In particular, the flat geometry and the excellent heat-conducting properties of the metal cassette supports a more, homogeneous thermal profile across the length, and height of bags during freezing, thereby enables a more consistent freezing process, compared to vials or bottles. Furthermore, immobilizing the bag during the freezing process decreases likelihood of bag breakages, and thereby contributes to the safety of the cryopreservation process.
Adequate quality control samples retained before cell therapy treatment are a crucial component of effective regulation and need to represent the conditions and history in the cryobag, containing the bulk therapy.4
References
- Chong E. et al.: CAR T cell viability release testing and clinical outcomes: is there a lower limit? Blood. 2019 Nov 21; 134(21): 1873–1875. Prepublished online 2019 Sep 25. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019002258. Available at. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6872962/
- Brewer R.: ATMPs and Annex 1: Some Answers, but More Questions, PDA. Available at: https://www.pda.org/pda-letter-portal/home/full-article/atmps-and-annex-1-some-answers-but-more-questions
- PDA: Manufacture of Advanced Therapy Medicinal Products for Human Use. Annex 2A. Available at: https://www.pda.org/docs/default-source/pda-europe-education-presentations/2022/07_eu00167-practical-application-atmps/pics-annex-2a-atmp-gmps-2022.pdf?sfvrsn=cc4f7481_2
- Meneghel J. et al.: Cryopreservation as a Key Element in the Successful Delivery of Cell-Based Therapies-A Review, Front Med (Lausanne). 2020 Nov 26:7:592242. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2020.592242. eCollection 2020. Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33324662/