What is autologous?
Table of contents
ShowYou may have come across the term “autologous” before in the context of stem cell therapy. Autologous stem cell transplantation is a type of cellular therapy that uses the patient's own stem cells to treat various types of blood cancers such as leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma. It uses knowledge from several medical fields, including oncology and hematology.
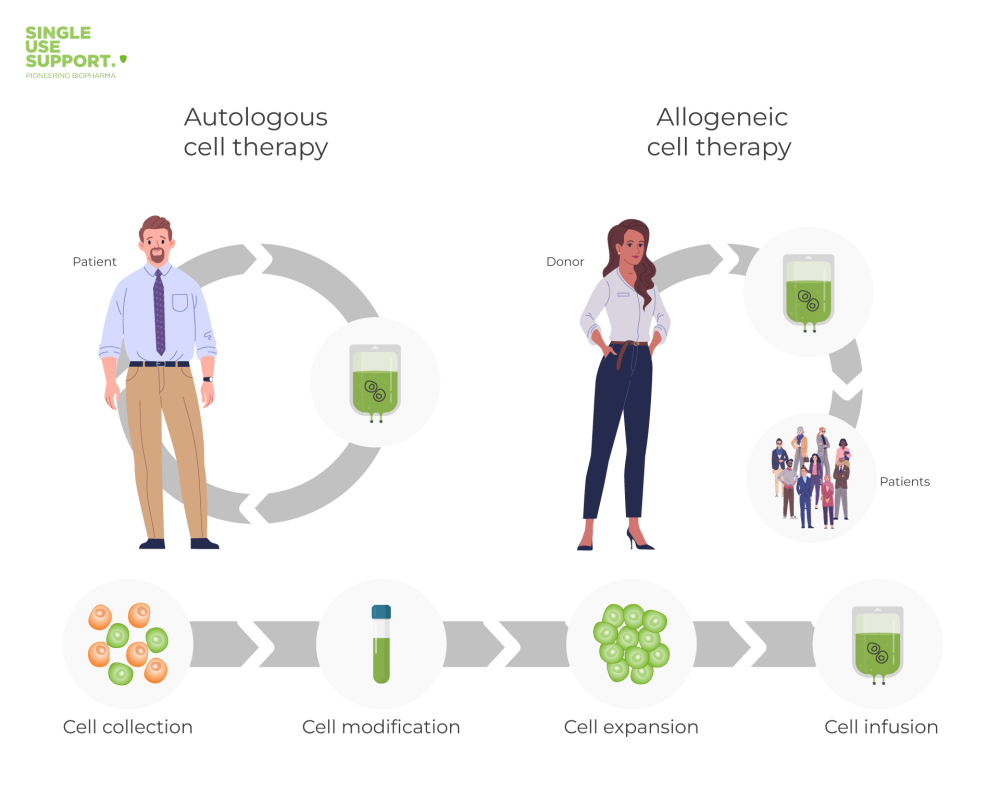
Besides autologous cell therapy, allogeneic cell transplant is another concept frequently used in medicine. Most importantly, autologous and allogeneic cell therapies can be distinguished by the type of cell donor. In autologous cell therapies, the cells derive from the patients themselves rather than being transplanted from a donor.
In this article, we will discuss what autologous stem cell therapy is, how it works, and its advantages and disadvantages over other types of stem cell transplantations.
Autologous – A brief definition
In order to give a definition of the word “autologous”, it pays off to have a look at its provenance. The term "autologous" comes from the Greek words "auto" meaning "self" and "logos" meaning "word" or "study." Therefore, "autologous" means "pertaining to oneself." In medical terminology, "autologous" refers to the use of a patient's own tissues or cells in a medical procedure, such as a transplant or cell therapy.
Autologous stem cell transplantation is a procedure that involves the collection and storage of the patient's own healthy stem cells before undergoing high doses of chemotherapy or radiation therapy to kill cancer cells. After the preparative treatment, the collected healthy stem cells are infused back into the patient's bloodstream to help the body produce new blood cells.
Autologous blood stem cells – why are they important?
Autologous blood stem cells are important because they are the building blocks of blood-forming cells in the body, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
When a patient undergoes high doses of chemotherapy or radiation therapy, these treatments can damage the blood-forming cells in the bone marrow, resulting in low blood counts.
Autologous stem cell therapy can help replace the damaged blood-forming cells with healthy stem cells, reducing the risk of infections and improving the patient's quality of life. An autologous stem cell transplant is often used to treat patients with blood cancers such as leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma, but it may also be used to treat other types of cancer.
Autologous cell therapy – the procedure
The autologous stem cell transplantation procedure involves three main steps: stem cell collection, stem cell storage, and application and recovery.
Collection of autologous blood stem cells
Stem cell collection usually involves a procedure called apheresis – a method where the patient's blood is filtered through a device that separates the stem cells from the other blood components. The stem cells are then collected and stored for later use.
Two typical sources of stem cells are the bone marrow transplant (BMT) and the collection of peripheral blood stem cells. While an autologous bone marrow transplant requires actual bone marrow to be harvested, stem cells can also be obtained from the bloodstream after prior mobilization from the bone marrow. Finally, stem cells can also be harvested from umbilical cord blood or the placenta.1
Stem cell storage
Stem cells are usually stored in a specialized facility that maintains the cells at a ultra-low temperature to keep them viable until they are needed. The stem cells can be stored for many years, depending on the storage conditions.
Application and recovery
After the preparative treatment, the stored stem cells are infused back into the patient's bloodstream through a catheter, similar to a blood transfusion. Engraftment, or the process of the new stem cells settling into the bone marrow and producing new blood cells, usually occurs within a few weeks after the transplant.
Advantages and Disadvantages Over Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation
Autologous stem cell transplantation is often compared to allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Allogeneic transplantation involves the use of stem cells from a donor rather than the patient themselves. Both methods have advantages and disadvantages.
Read also: What is allogeneic?
The main advantage of autologous stem cell transplantation is that it does not involve the risk of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), a potentially serious complication where the donor's immune cells attack the patient's healthy tissues. Because the patient's own stem cells are used, there is also a reduced risk of rejection by their immune system.
However, one of the main disadvantages of autologous stem cell transplantation is that it does not provide the benefit of graft-versus-tumor effect. This effect describes a donor’s immune cells fighting tumor cells in the patient’s body and can be achieved with allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Additionally, if the patient's cancer cells are present in the collected stem cells, the transplant cannot be used in treating the cancer.2
Autologous Stem Cell Storage – A Matter of Temperature
Once the autologous stem cells are collected, they need to be stored until they are needed for transplantation. Proper storage is critical for maintaining the quality of the stem cells.
The process of freezing and thawing stem cells can be complex and requires specialized equipment and expertise. Here is where Single Use Support comes into action: With an entire product line-up for ultra-cold freezing, storing and shipping, the demands of highly sensitive cell therapies in terms of temperature consistency can easily be met. Additionally, Single Use Support's solutions for automated filling are able to deal even with minute units.
While the cryogenic freezer RoSS.LN2F is able to freeze products down to -180 °C in a controlled manner, stem cells are ready for cryopreservation with or without liquid nitrogen until the stem cells are due to be thawed and applied. Until then, they are kept safe by specialized primary packaging solutions, protecting them from potential mechanical stress and contributing to high product quality.
FAQs
What is an autologous procedure?
An autologous procedure is a medical treatment that uses a patient's own tissues or cells.
What are examples of autologous?
Examples of autologous procedures include autologous stem cell transplants, blood transfusions, and tissue transplants.
What is the difference between autologous and allogeneic?
While autologous stem cell transplantation uses the patient’s own cells, allogeneic cell therapy uses a transplant from a donor.
- Harvesting blood stem cells for transplantation, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279428/, Published 2013
- Graft versus tumor effects and why people relapse, http://dx.doi.org/10.1182/asheducation-2017.1.693, Published 2019-04-17