mRNA cold chain: considerations & solutions for safe handling
Table of contents
ShowmRNA (messenger RNA) technology has emerged as a groundbreaking innovation with vast potential across various fields, including healthcare and biologics. However, it also raises questions on the ideal freezing, storage and transport conditions for mRNA, considering the high temperature sensitivity of mRNA.
This article explores the critical aspects of cold chain management in ensuring the efficacy and safety of mRNA-based products, including vaccines and therapeutics.
Understanding mRNA – applications and cold chain considerations
mRNA is crucially involved in protein synthesis within cells. Beyond vaccines, mRNA technology holds promise in various areas, including gene therapy, cancer treatments, and regenerative medicine.
Messenger RNA is highly sensitive to external factors such as temperature fluctuations, light exposure, and mechanical stress. Maintaining the cold chain is crucial to preserve the integrity and stability of mRNA products throughout the supply chain, from manufacturing to storage and transport.
Cold chain management for mRNA products
mRNA products are not only sensitive to physical stress, but first and foremost to degradation due to unsuitable cold chain handling, including freezing conditions and storage temperatures. These products, therefore, require freezing devices, cold chain storage and transport that are able to meet their high temperature requirements.
Temperature control and storage conditions
Maintaining the appropriate temperature range is crucial for mRNA stability. Depending on the specific mRNA product, storage conditions may vary from ultra-cold temperatures (-70°C or below) to standard refrigeration (2-8°C). Proper cold chain equipment, such as specialized freezers and refrigerators, is essential.
In terms of temperature, control and precision are key: Already during drug development, clinical trials are conducted in order to determine the freezing and storage requirements of specific mRNA-based formulations, also referring to the most suitable freezing rates and storage temperature – be it ultra-cold or room temperature. It is vital to meet the previously stated temperature requirements, also in order to stay within the regulatory frame provided by the Food And Drug Administration or the World Health Organization.
Read more about: Best practices in freezing mRNA
Ultra-cold freezing and thawing protocols
Certain mRNA products, especially those used in vaccines, require optimized cold chain conditions including ultra-cold storage to prevent degradation. Thawing protocols must be carefully followed to avoid compromising the integrity of mRNA.
When the manufacturing process of a product requires an ultra-cold chain, this implies freezing substances down to temperatures as low as -70 °C. In order to avoid deterioration and damaging effects of ultra-cold temperatures, freezing and thawing protocols must be followed, determining the ideal freeze/thaw rates. These protocols are conducted with dedicated freezing devices that are able to lower a product’s temperature in a controlled manner, as this is essential to maintain their viability.
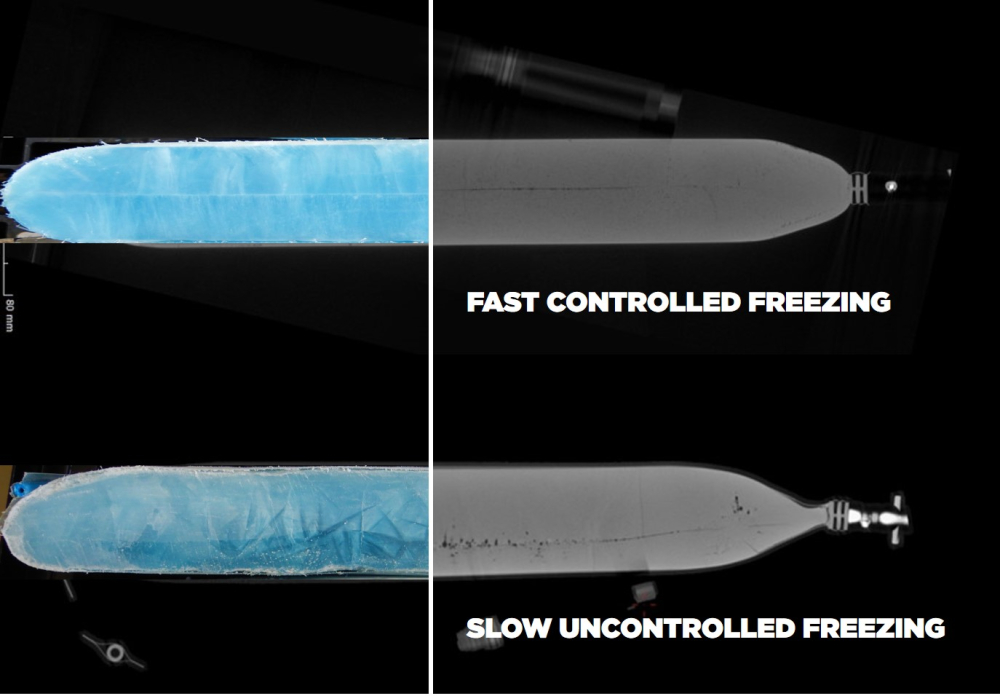
In recent years, plate freezing has proven to be an advantageous approach to freeze pharma products down to ultra-cold temperatures. Compared to traditional blast freezing techniques, plate freezing offers controlled and fast freezing rates, which helps to avoid cryoconcentration and other potential damaging effects of ultra-cold freezing.
Cold chain packaging and transportation
Protective packaging, insulated containers, cold boxes and temperature-controlled shippers are essential to maintain the cold chain during transportation. Proper labeling and handling instructions help ensure the mRNA products are handled correctly.
Protective storage solutions help to avoid product loss that might otherwise occur due to leakage of single-use assemblies, as these can break more easily when subjected to ultra-cold freezing. Additionally, staff and the environment must be protected from contamination with sometimes hazardous substances.
Also financial aspects need to be taken into consideration, especially when drug production is brought to a larger scale. Efficient packaging solutions are, therefore, just as indispensable as reliable, stackable and scalable cold storage solutions.
Real-time monitoring of temperature
Continuous monitoring of temperature throughout the cold chain is on demand. Advanced monitoring devices and systems provide real-time data, alerting stakeholders to any temperature deviations or transportation delays that may impact the efficacy of mRNA products.
Storage of mRNA vaccines during the COVID-19 pandemic
The storage of mRNA vaccine products, such as those developed by Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna, played a vital role in the fight against the COVID-19 pandemic caused by the coronavirus. Their proper storage ensures the efficacy and availability for vaccine distribution to combat the spread of the SARS-CoV-2.
COVID-19 vaccines like the Pfizer vaccine or the Moderna vaccine consist of lipids carrying specific mRNA segments and are typically stored in specialized vials designed for vaccine storage. These vials are carefully sealed to maintain mRNA integrity. Strict vaccine storage protocols are followed to preserve their effectiveness.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, vaccine storage has become a critical component of the emergency response in the public health sector. The vaccines have initially been authorized for emergency use to expedite their distribution and administration. As a result, the vaccine supply chain had to be carefully managed to ensure timely vaccine delivery to healthcare providers and immunization centers.
Both the Moderna COVID vaccine and the Pfizer vaccine have specific shelf life considerations. Beginning with vaccine manufacturing, such products must be stored at appropriate temperatures to maintain their efficacy. The storage conditions include temperature control within specified ranges and protection from light exposure.
Challenges and solutions in mRNA cold chain management
Considering their high demands in terms of storage conditions, mRNA products pose several challenges for manufacturers and suppliers. Some of the most important aspects include:
Maintaining ultra-low temperatures – Sustaining ultra-low temperatures presents a significant challenge in mRNA cold chain management. Innovative solutions, such as the use of specialized storage freezers and the targeted use of dry ice for transportation, can help maintain the required temperatures during storage and transportation.
Ensuring proper cold storage infrastructure – Investing in state-of-the-art cold storage facilities is vital to safeguard mRNA products. These facilities should meet stringent standards, including adequate insulation, temperature control, and backup systems to mitigate any potential disruptions. However, there are innovative, modular and pallet-sized systems on the market that help circumventing the need for laborious and costly structural adaptations.
Collaboration in the supply chain – Effective cold chain management requires collaboration among stakeholders, including CDMOs, manufacturers, logistics providers, healthcare providers, and regulatory authorities. Establishing transparency, clear communication channels and standardized procedures must ensure a seamless cold chain.
Regulatory compliance and guidelines – Regulatory bodies, such as the FDA, provide guidelines and regulations specific to mRNA products' cold chain management. Furthermore, transportation has to comply with ASTM D4169 and ISTA regulations. Adhering to these guidelines ensures compliance and the highest quality standards, but requires both equipment, know-how and resources.
Advancements in mRNA cold chain management
In order to tackle the aforementioned challenges, elaborate cold chain management has been developed and continuously improved. Advancements in cold storage equipment, including devices for safe and controlled freezing, ultra-cold storage freezers and temperature-controlled containers, contribute to enhanced cold chain management. These technologies offer improved temperature stability, reliability, and energy efficiency.
Real-time temperature monitoring systems with wireless connectivity enable stakeholders to track and analyze temperature data throughout the cold chain. This data-driven approach allows for proactive interventions and ensures optimal storage conditions.
Innovative packaging materials and insulation techniques, such as phase-change materials and advanced thermal barriers, help maintain temperature stability and protect mRNA products from temperature fluctuations.
The future of mRNA cold chain management
As mRNA technology advances, scalability and commercial production become essential considerations. Developing efficient and scalable cold chain solutions will be critical to meet the increasing demand for mRNA-based products.
Ensuring equitable distribution and global access to mRNA products require robust cold chain infrastructure and collaboration among nations. Addressing logistical challenges and implementing efficient distribution networks will be crucial, with high regards to the circumstances and possibilities in different countries.
As the use of mRNA technology expands, addressing sustainability and minimizing the environmental impact of cold chain operations will be imperative. Exploring greener alternatives, optimizing energy consumption, and reducing waste will play a vital role, with single-use technology in mRNA manufacturing as an emerging approach to enhance sustainability, but also cost-effectiveness and process safety.

Advanced mRNA cold chain management with Single Use Support
As illustrated in this article, the challenges related to mRNA manufacturing are manifold. Due to its temperature sensitivity, cold chain management of mRNA-based products can be laborious, cost-intensive and requires broad knowledge as well as trained staff.
With the aim to facilitate and streamline mRNA processing, Single Use Support has established a product line-up that allows automated processes and high levels of efficiency, scalability and sustainability.
With a plate freezing platform, fast and controlled freezing rates help to achieve the desired freezing results and avoid effects like cryoconcentration. It is designed to freeze different volumes of drug substances, contained in single-use bags in different sizes. And with the protective RoSS® Shell, mRNA products are provided with an additional layer of protection, as this robust shell covers single-use bags for storage in ultra-cold storage freezers and shipping in dedicated shipping containers.
With cold chain process solutions like these, Single Use Support contributes to the fast progress in the field of mRNA and helps to make this promising technology more accessible.









