Reducing human errors and technology failures in biopharma
Table of contents
ShowReducing human errors is crucial in drug substance management, as they can be fatal and costly mistakes, even more so when they happen to employees in the medical and/or pharmaceutical fields.
However, it is not only different types of human errors but also faulty equipment that can have enormous consequences for biopharmaceutical companies. If a batch is lost due to contamination – irrespective of whether it was caused by employees or faulty equipment, the manufacturer will likely suffer significant financial losses, but, even more fatally, this can lead to dire consequences for the patient relying on the specific medication.
And that is just one of the reasons why there are strict guidelines and regulations in place on how to deal with potential errors and the resulting impact on product quality or other consequences. Once an error report is issued, predefined corrective and preventative measures are to be implemented.
Human error reduction – essential in biopharma risk management
The reduction of human error in the production of biopharmaceuticals is an indispensable cornerstone in a holistic risk management system, as such errors are far more meaningful than simple lapses and slip-ups, and often difficult or impossible to repair. Therefore, reducing human errors in the first place is necessary to avoid the loss of drug product as well as quality issues.
After a thorough root cause analysis of where human errors might occur along the production process (depending on the amount of human performance required in the process), manufacturers need to implement strategies to reduce the risk of human error within respective tasks. At this point, quality control and the evaluation of corrective actions is as important as to regularly train employees. This regular training should aim to create awareness of common causes for errors along the workflow and human error prevention.
Read more: Biopharma supply chain – 7 risks to be aware of
In addition to proper training, checklists are helpful to guarantee GMP compliance of not only standard operating procedures, repetitive tasks and a secure work environment, but the entire production process. Furthermore, technological solutions can be implemented on various process steps to reduce the risk of human error.
Analyzing and eradicating potential sources of errors
A survey conducted in June 2020 showed that deviations in the filling process can be traced back to three leading causes.
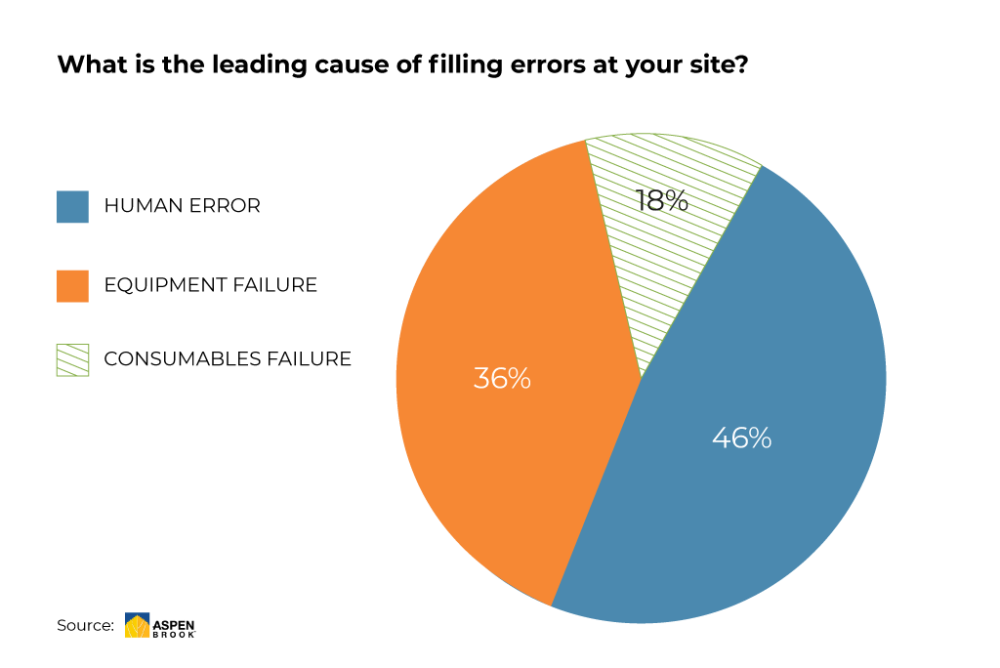
Source: Aspen Brook (preliminary results, June 2020)
The most effective way to deal with such issues is to eradicate potential sources by adapting the implemented technologies and systems so that interaction with humans can be reduced to a minimum, and at an even earlier stage, by implementing integrity tests that make sure your consumables are not faulty.
Agile and flexible single-use systems
In recent years, technologies and platforms based on disposable single-use components have found their way from the lab – where they were initially employed – to mainstream production. An ever-growing number of pharmaceutical manufacturers is moving away from traditional tanks and implementing more flexible and user-friendly options:
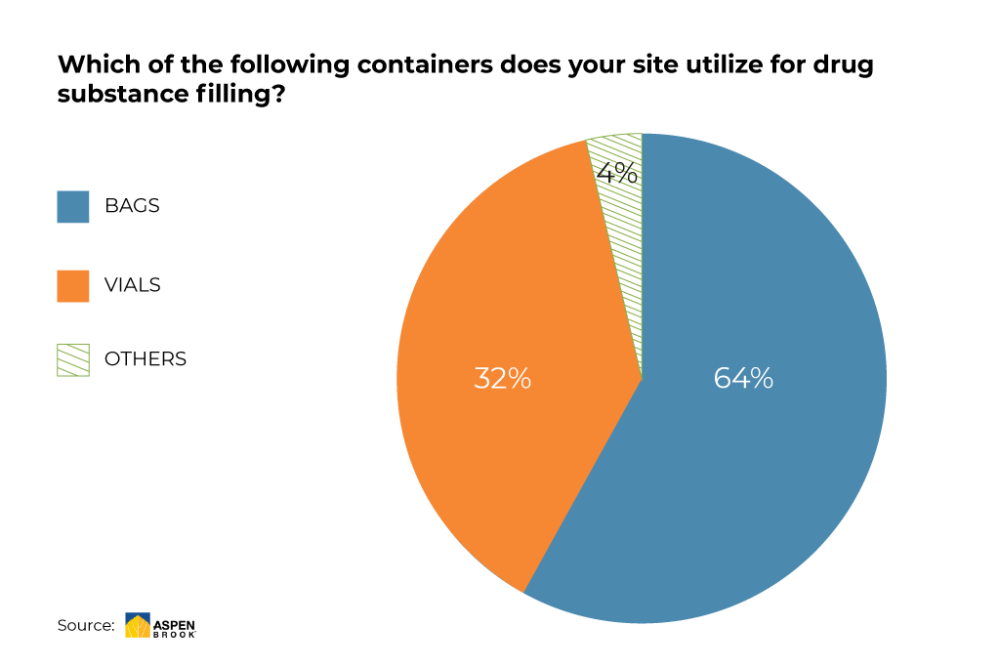
Source: Aspen Brook (preliminary results, June 2020)
Single-use technologies allow manufacturers a great level of flexibility and scalability when applying predefined actions during the nurturing of cells as well as the entire drug substance logistics process from filling to dispensing to shipping.
Standardized yet scalable solutions to eliminate potential sources of errors and failure
While the number of manufacturers employing manual filling processes is still surprisingly high, there is a growing trend towards utilizing more reliable automated systems.
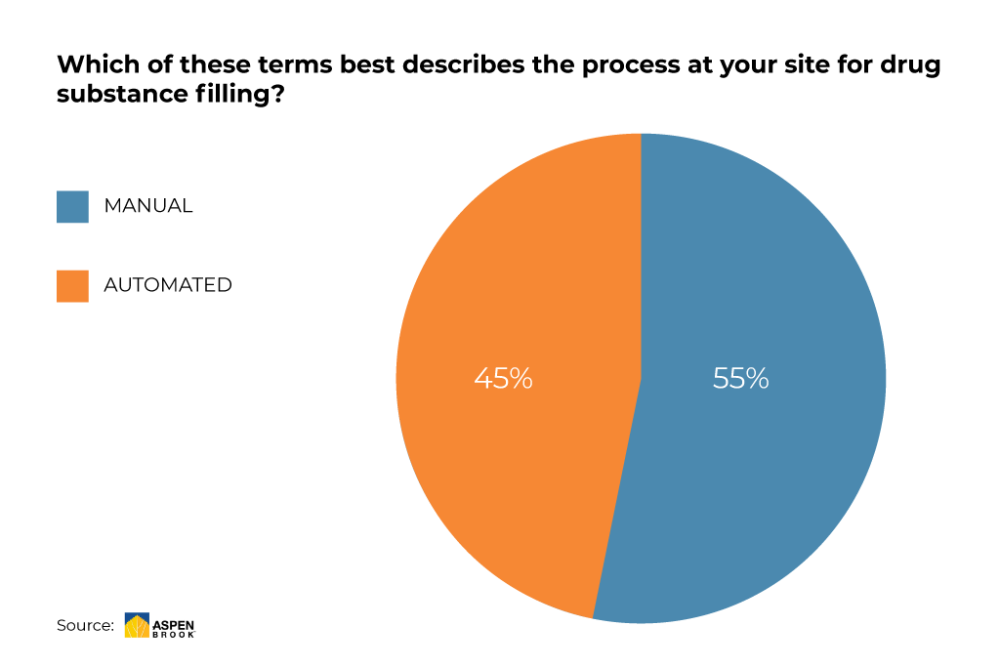
Source: Aspen Brook (preliminary results, June 2020)
While being based on a standardized concept, the utilization of single-use components turns such systems into highly agile platforms that can be scaled to serve a number of purposes and basically any required volume. This is the perfect prerequisite for platforms that are used across the spectrum – from lab and study purposes all the way to small-scale and/or blockbuster production, offering the highest possible level of precision for both small batches and vast quantities.
It makes a big difference whether process steps such as seed train intensification, integrity testing, filtering or dispensing require human assistance or whether they can be fully automated in-line to take away a potential source for human error while at the same time increasing reliability and output.
Further advantages of process automation to reduce human error
Additionally, automated processes on the basis of single-use technologies can reduce the risk of contamination by reducing or fully eliminating cleaning and maintenance.
It seems that the success of single-use technologies geared towards the biopharmaceutical sector is only logical to continue, given the long list of benefits they offer over traditionally used systems. If you want to find out how to streamline your processes with a scalable platform while at the same time reducing or eliminating potential sources for errors and failures, check out our automated processes.
In other industries, the source „human error” is reduced by 30% to 60% using consistent process automation. Wow.
FAQs
What is the meaning of reduction of human error?
The reduction of human error is of great importance in biopharma processes such as the production of drug substances. As these products often come with high value and timely deliveries can be crucial in the treatment of many patients, measures have to be taken to avoid human errors.
Furthermore, certain drug products can pose risks to employees as well as to the environment, which is why the risk of leakage and contamination has to be minimized.
How can errors in the workplace be reduced?
There are several ways to reduce errors in the work space, very individual to specific fields. For biopharma companies, for instance, reducing human errors in production processes requires employees to be trained on the potential risks and how to avoid them. Also, potential risks have to be identified in order to define methods that minimize these methods. Furthermore, several manual interventions can be replaced by automated solutions, specially designed for the integration in these delicate processes.










